How ADS-B data facilitates sustainability efforts in aviation
The aviation industry faces growing pressure to reduce its environmental impact, which requires innovative approaches and precise data to support sustainable practices.
One such data source, Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B), has become essential for tracking and optimizing aviation emissions. Often associated with air traffic management, ADS-B data offers much more than positional information—it provides detailed insights into flight paths, fuel consumption, and emissions. By using ADS-B data, the aviation sector can monitor environmental impacts more accurately and implement strategies to minimize fuel use, reduce contrails, and lower emissions. Here’s a closer look at the transformative impact of ADS-B data on achieving greater environmental sustainability in aviation.
Contrail forecasting and monitoring
Contrails, those line-shaped clouds produced by aircraft exhaust, can significantly affect the atmosphere. Leading this innovative approach are organizations like Spire and Estuaire, which integrate ADS-B data with suite of web applications supporting airlines, lessors and aviation lenders in measuring and reducing their environmental impact.
Spire harnesses an extensive network of satellites combined with terrestrial data inputs to gather comprehensive aircraft positional data. This data is compiled into Flight Report, which compiles hundreds of millions of daily satellite and terrestrial ADS-B positions into a streamlined, one-row-per-flight format that includes comprehensive flight and aircraft data, tailored for post-flight analytics and reporting purposes. In collaboration with Estuaire, which specializes in the monitoring and analysis of aviation emissions (CO2, non-CO2, and lifecycle effects), Spire’s data enriches the understanding of flight routes and operations. This collaboration delivers precise, historic flight insights, crucial for a detailed and accurate evaluation of the environmental impacts associated with each flight.
Fuel consumption & carbon emissions
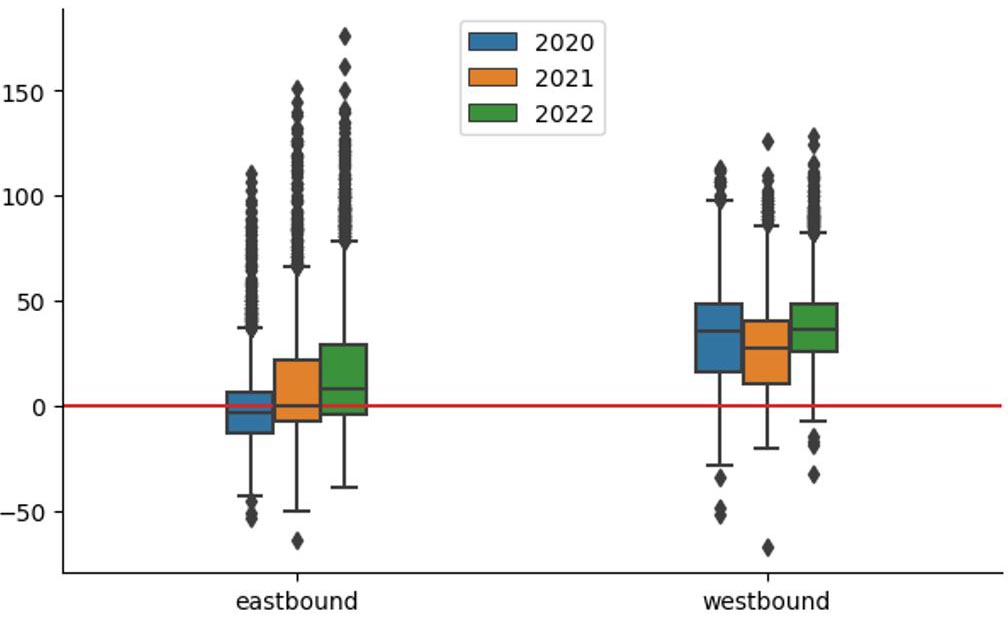
ADS-B data is also instrumental in analyzing and optimizing fuel consumption and carbon emissions. A study by Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) and Spire Global investigated how flight emissions are influenced by upper wind components – wind speed and direction of the wind at high altitudes – over the North Atlantic Ocean.
Dr. Junzi Sun’s research utilized space-based ADS-B data from Spire’s LEMUR satellites, combined with historical weather forecasts, to reconstruct accurate 4D flight trajectories. The study revealed how ADS-B data in combination with weather data contribute to more accurate assessment of emission at the flight level.
Difference in CO² estimation (ton/flight)
To enhance the understanding of different complexities to accurately map out the spatial and temporal distribution of aviation emissions, Imperial College London leveraged ADS-B telemetry from Spire Aviation to develop the Global Aviation Emissions Inventory (GAIA), cataloging over 103.7 million unique flight trajectories between 2019 and 2021. This inventory examines how emissions correlate with flight distances, explores regional variations in fuel consumption, and highlights the differences in emissions between short-haul and long-haul flights. This advanced insights significantly improve the accuracy of assessing non-CO2 impacts associated with global aviation activities.
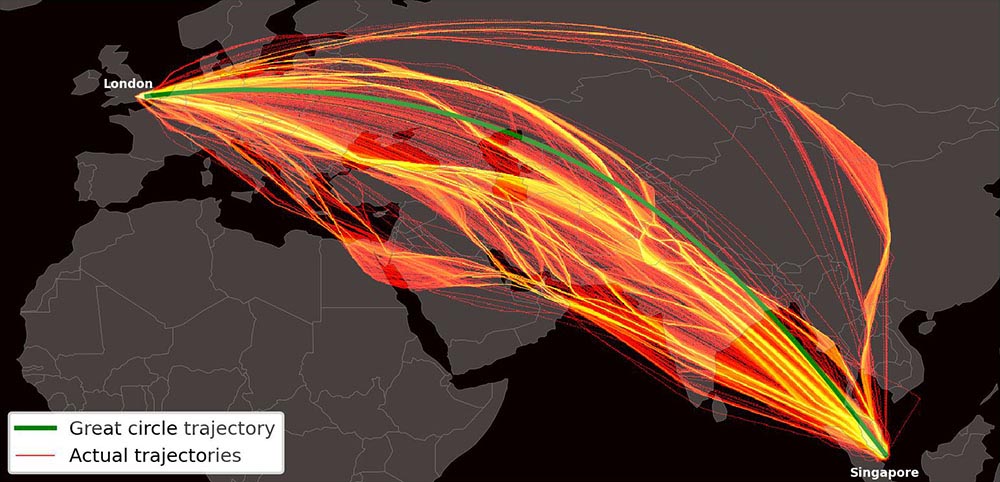
The impact of comprehensive and real-time ADS-B data
The real-time precision and comprehensive coverage of ADS-B data allow for continuous monitoring and detailed analysis of flights. This enables a deeper understanding of how different factors—such as aircraft type, passenger load, wind conditions, and engine efficiency—affect fuel consumption and emissions on specific routes. By identifying these variables, airlines can optimize flight paths, improve operational efficiency, and ultimately, reduce their environmental footprint.
Conclusion
ADS-B data is more than just a tool for air traffic management; it’s a pivotal component in the aviation industry’s journey toward sustainability. By enabling more accurate emissions tracking and offering insights into environmental impacts at the flight level, ADS-B dataset helps create a foundation for actionable strategies to achieve greener aviation practices. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of ADS-B data will undoubtedly expand, further supporting global efforts to make aviation more sustainable.
 Written by
Written by