Aviation GNSS interference
Utilize ADS-B navigation accuracy reporting for Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) interference intelligence and monitoring
We leverage AI and ML technologies, predictive modeling, and our proprietary satellite constellation to deconstruct raw ADS-B data (NIC/NACp) and turn it into actionable intelligence with the highest level of accuracy. We also pair our ADS-B data with additional aircraft, flight, and weather information, which can be deployed to satisfy needs in flight operations, geospatial intelligence, border management, insurance risk management, applications development, financial analysis, travel analytics, tourism, and more.
Book a call with our experts
Navigating the challenge: GNSS jamming
The threat
GNSS jamming
GNSS jamming poses significant threats to the safety and efficiency of those operating in the air domain, potentially compromising everything from airline operations to national security.
The response
GNSS interference mapping
By thoroughly mapping airspace where a navigation system might be compromised, those with a stake in the airspace and aircraft safety can strategize to mitigate the operational and asset risks.
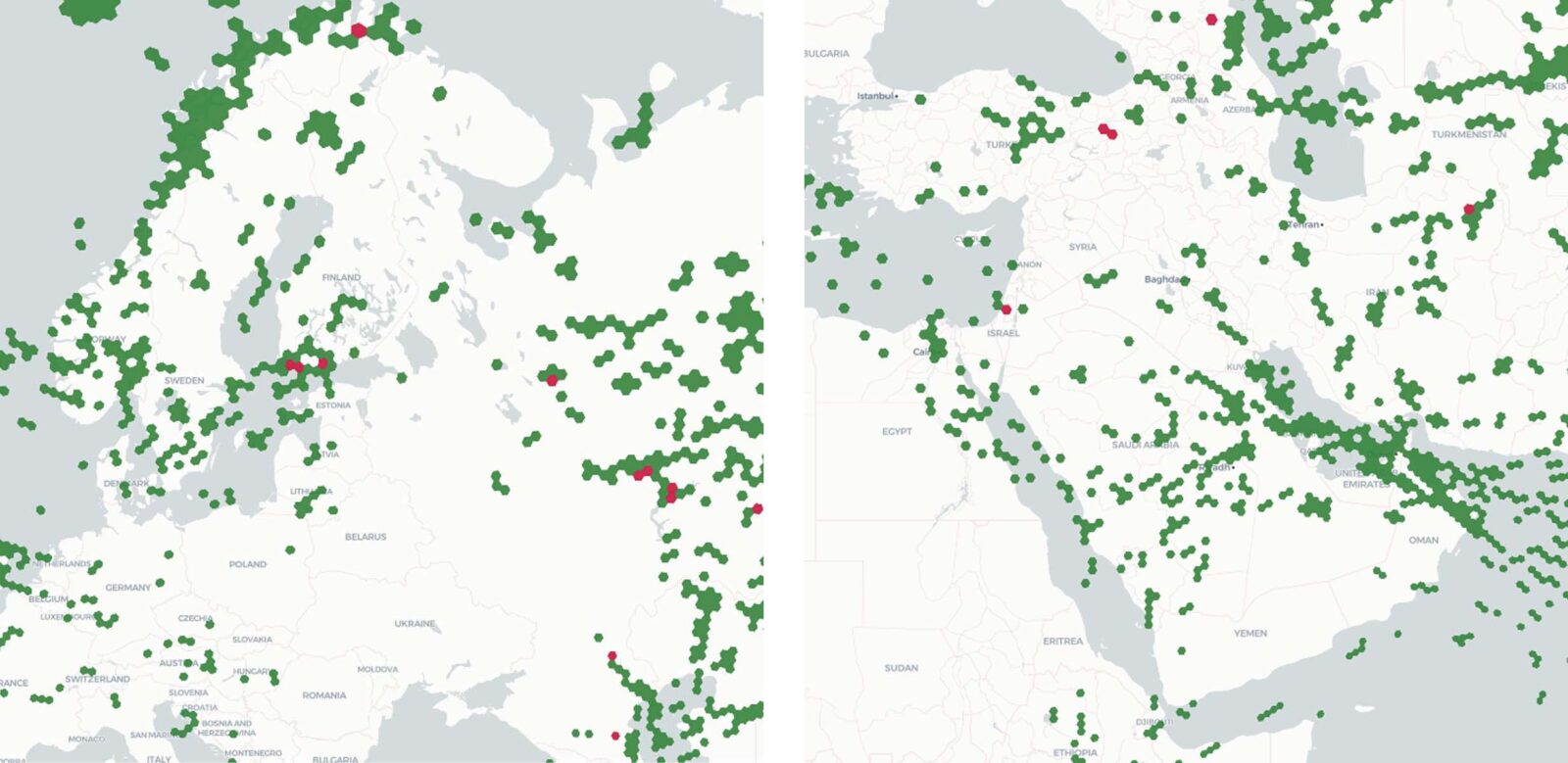
GNSS coverage over Ukraine and Middle East showing good GPS signals (green) and GPS jamming locations (red)
Identifying GNSS interference with ADS-B
Publicly available GNSS interference maps are built on open-source ADS-B data collected from Spire’s satellite and ground-based receivers. Space and ground-based data fusion provide a global baseline for intelligence in a variety of locations such as conflict zones, low-air-traffic spaces, open oceans, and mountain ranges, which otherwise lack the data to make clear and actionable observations.
“Satellite-based ADS-B monitoring and interference mapping can clear the fog and provide a clearer picture of potential GNSS interference.”
GPS interference map:
The Spire advantage
Comprehensive datasets. Unmatched intelligence.
Spire owns and operates one of the most expansive constellations of small satellites in LEO, equipped with ADS-B receiver payloads that work around the clock to collect and disseminate data for the most comprehensive GNSS interference mapping and characterization on the planet.
Unmatched GNSS interference awareness
- Near-global ADS-B data coverage – 24/7
- ADS-B data collection where terrestrial services fail
- Real-time flight tracking data (ADS-B)
- Real-time weather activity
- Historical flight and weather data (xyrs)
- Flight tracking & historical data APIs – easily integrated for efficiency and project success
How does GNSS mapping work?
Using data collected by our ADS-B receiver payloads deployed across a range of low-earth orbits, Spire can identify, assess, and map potential GNSS interference hotspots with varying degrees of risk at every corner of the planet.
We use two primary categories of ADS-B data to determine and calculate the risk within a potential GNSS interference zone.
Navigation Integrity Category (NIC)
NIC data indicates the horizontal containment radius around an aircraft, sent in the airborne position message every 0.4-0.6 seconds. NIC anomalies occur when the aircraft’s position is not guaranteed, with a 99.999% probability, to be within the horizontal protection level of the containment radius. The bigger the containment radius, the smaller the probability percentage.
NIC ≥ 7: Normal circumstances
NIC = 0: ADS-B system’s setting is wrong or GNSS is severely affected by a jammer
Navigation Accuracy Category Position (NACp)
NACp data provides an aircraft’s estimated vertical and horizontal position uncertainty (EPU), sent in the operational status every 2.4-2.6 seconds. NACp anomalies occur when the aircraft’s actual position does not fall within the estimated position 95% of the time and are considered a good indicator of when an aircraft’s GNSS transponder is malfunctioning or when a GNSS signal is being jammed.
NACp = 0: No GNSS reception or jamming
Since NACp data is broadcast less regularly than NIC data, NIC data ensures each NACp position has an associated quality indicator, helping validate concerns over NACp anomalies.

