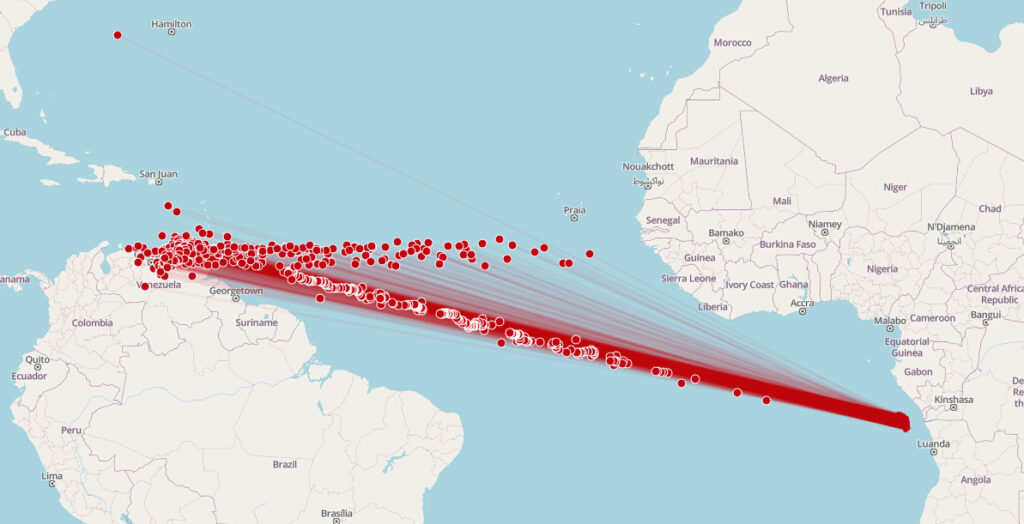
Reconnaissance satellite constellations: For enhanced global awareness
We live in a world where data drives decisions and insights shape strategies, and today, the power of tailored satellite technology is transforming industries at unprecedented rates.
Those tasked with operational decision-making now recognize that nearly every challenge requires unique solutions, and many are beginning to use independently owned satellite constellations to meet their needs.
Governments, in particular, are increasingly interested in independent satellite constellations – mainly due to the fact that they allow them strategic autonomy and control over data and critical infrastructure.
Now, even nations with little or no existing satellite infrastructure can explore space-based strategies – something that was not possible just a short time ago. With more and more space-as-a-service companies shifting toward tailored, off-the-shelf satellites that can be launched and operated with speed and affordability, we can expect to see more governments taking advantage of the opportunity.
At Spire, we’re on a mission to do just that: deliver world-class, mission-specific solutions with satellite-enabled technologies that can be constructed, deployed, and operated with speed and precision.
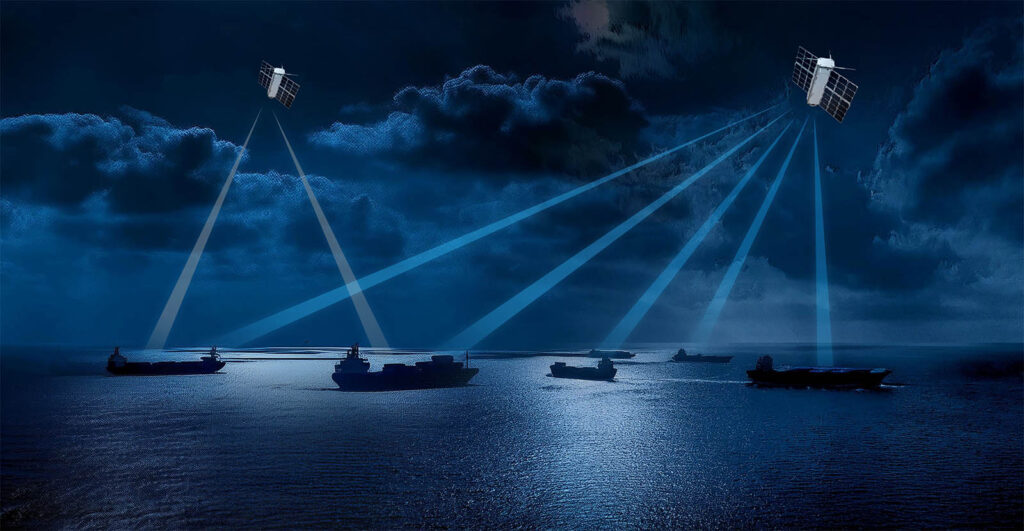
Whether for accurate and timely geolocation of vessels in the maritime domain, detection of GNSS jamming and spoofing on land or at sea, or global-scale climate monitoring, we help our clients build tailored satellite constellations to deliver unparalleled data-backed insights.
About Spire’s independent satellite constellations
Here at Spire, we’ve solidified our position as one of the global leaders in the development and deployment of independent satellite constellations – designed to meet the specific needs of various industries and applications.
How can we say we are global leaders in independently owned and operated constellation solutions?
We’ve developed lasting relationships with innovative and impactful organizations around the globe, supporting some of the world’s most demanding applications with critical data and space infrastructure.
Our tailored constellations enable entities to gather precise, mission-specific data in near real-time, enabling unmatched decision-making based on complex data rather than a hunch. Since our constellations can be built with specific payloads and tasked to mission-specific applications, it allows users in nearly every industry to drive growth and facilitate profits.
Spire x Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC): Enhancing RF geolocation from LEO
Spire recently partnered with the Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC), a trusted leader in aerospace, defense, and electronics solutions, to grow their network of RF-enabled satellites and enhance their ability to locate Earth-bound RF emission sources from Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Spire’s cluster of four 6U satellites helps SNC detect and geolocate objects near the Earth’s surface using radio frequency (RF) emissions, to enhance government and military insights into RF interference threats and develop strategies to limit risks.
Spire’s independent satellite constellations allow SNC to improve its RF detection capabilities with secure, scalable, and proven RF technologies. Since SNC can task the 6U cluster for specific objectives, it allows a more affordable, more flexible approach to LEO-based missions.
Paired with SNC’s 12+ years of experience developing algorithms, analytics, and process automation, Spire aims to showcase how its independent LEO-based satellites can successfully address the growing market need for RF data collection and analysis.
Spire satellite formations and functionality
Spire’s tailored constellations can be configured in various formations, be it clusters of two, three, or four – or a series of satellites flying in an “orbital plane.” Configuration flexibility allows for the creation of hyper-specific solutions that not only maximize data coverage but also ensure collection accuracy and efficiency.
Satellite clusters
Each cluster, regardless of configuration, is designed to work cohesively. The clusters are tailored using geolocation techniques like triangulation, TDOA, and FDOA – all of which deconstruct data alongside one another for high-level insights. The satellites within each cluster can be adjusted dynamically to adapt to evolving mission needs or environmental conditions, ensuring that the data delivered is relevant and actionable.
Satellite clusters typically operate in a triangle or box formation. By orbiting the Earth in a consistent formation, they are able to execute data collection and deliver insights with a higher level of accuracy than just one satellite.
An example of this would be when an entity like the US military needs to identify the source of new or recurring GPS interference. When GPS interference (RF interference) occurs, unusual RF emissions in the GPS frequency range are typically present. Our GNSS-R payloads are designed to capture these emissions, and using a TDOA/FDOA approach, we can geolocate the source of the emissions (typically a GPS jammer) with a high level of accuracy.
Satellites orbiting “in plane”
The other way we maintain orbit for our mono-satellite constellations is through satellite drag and other satellite operation techniques, including propulsion when required for a specific customer mission. In this formation, satellites orbit the Earth in a linear pattern, allowing data to be collected continuously over a broader scale. This helps monitor larger areas of the planet and is particularly beneficial for continuous monitoring of things like climate and other environmental parameters.
An example of this would be atmospheric phenomena like hurricanes. By maintaining a consistent orbital plane, these satellites can provide continuous data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and cloud cover across vast regions. This real-time data is crucial for predicting weather patterns and issuing timely warnings, significantly enhancing disaster preparedness and response.

Spire Satellite constellation technical specifications
Our constellations are incredibly flexible and ready to scale, allowing our customers to deploy new platforms to collect and process data on board. Our customers can conduct in-orbit feasibility trials and add new dimensions to existing infrastructure without overhauling the systems.
Our customers control their payloads directly through a proprietary API without human intervention. Their commands and data flow through the Spire network, fully encrypted, with the option to add a second layer of client-side encryption using keys that only the customer controls.
Further, our satellite constellations are equipped with off-the-shelf ISR products that can be deployed in as little as nine months, allowing any organization or national agency to build its own state-of-the-art intelligence capabilities when needed.
View Spire’s satellite constellation product offers
Spire’s Constellation Management Platform
Spire’s Constellation Management Platform (CMP) is the go-to tool for customers to streamline satellite control – automating constellation operations, simplifying tasking, and enabling real-time communication with all space assets. Our CMP improves customer accessibility through seamless connection to Spires proprietary API and allows your team to focus its time and resources on assessing mission data.
To learn more about how we can simplify space anywhere, anytime, be sure to visit our Constellation Management Platform page. You can book a call with a Spire consultant or explore a platform demo to see how it can help manage your mission.
Who we serve
With 14+ years of experience serving clients in government & military, maritime, weather & climate, and aviation, Spire offers actionable intelligence with real-time data for customers in nearly every industry.
Government and Defense
Over the years, we’ve helped facilitate and progress NASA missions, unearth strategies used by drug cartels to bring illicit contraband across borders, and delivered RF interference insights to the US military that support national security and defense.
While terrestrial defense systems can help secure borders and coastal areas, their limitations cap their impact. With the rise of mission-specific satellite constellations, governments, militaries, and maritime authorities can task satellites for hyper-specific and global-scale purposes – bypassing the physical and geographic limitations involved with terrestrial systems.
What makes Spire’s capabilities so impactful?
- Unclassified data sharing: Often, when government agencies need to share specific data, they are unable to do so due to the strict security regulations in place. Since Spire’s constellations are private and free of these regulations, government customers and their allies can send and receive data without violating laws. Not only is Spire able to legally support this type of data-sharing, but our constellations and data networks can do it with incredible speed, streamlining communications between government branches and global allies.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) monitoring: As part of the Constellation Management Platform, Spire’s standardized API tool helps customers manage and track project KPIs, providing real-time asset performance insights and optional deviation alerts. The SLA also offers schedule and performance guarantees, providing baked-in reliability that ensures confidence in the system’s operational performance.
Maritime organizations
Our independent satellite constellations support maritime organizations with offshore asset surveillance, commodity and market intelligence, warfare intelligence, flag administration support, and more.
One of the biggest advantages of mission-specific constellations in the maritime industry involves identifying and tracking vessels in real-time using Radio Frequency (RF) data collection – which is crucial for monitoring ship routes and ensuring asset safety at sea.
The high-performing RF payloads aboard our LEO satellites capture data in a wide range of frequency bands, including UHF, S-Band, X-Band, Ku Band & Ka-Band. This wide range of data capture allows us to decipher ship positions when signals are spoofed, jammed, or halted, and we deliver the insights promptly and with near-global coverage.
Aviation safety and security
GNSS interference is a rapidly growing threat in the aviation industry, which affects everything from civilian flights to military operations. GNSS jamming and GNSS spoofing are both increasingly common tactics being used that are affecting the safety and security of those operating or managing aircraft, so being able to identify the source of this interference and make better-informed decisions is becoming increasingly important.
One of Spire’s goals for the future is to help secure the aviation and security sectors, and we are doing it with the enhanced detection and geolocation of GNSS interference signals.
To do this, we leverage our growing satellite constellations, advanced payloads, and advanced AI and ML algorithms to take raw ADS-B data (primarily from commercial aircraft) and categorize it by interference likelihood and threat level, allowing air traffic controllers and pilots to operate confidently and better manage risk.
Spire’s capability to collect more reliable ADS-B data through miniaturized LEO satellite and TRL 9 sensor technology allows us to build a constellation that can offer near real-time, global coverage. All the collected data is cataloged and can be accessed by our clients for historical data insights and trend analysis.
We also pair our ADS-B data with additional aircraft, flight, and weather information, which can be deployed to satisfy needs in flight operations, geospatial intelligence, border management, insurance risk management, application development, financial analysis, travel analytics, tourism, and more.
Weather and Climate entities
It’s no secret that the changing climate is taking a severe toll on people and the planet. Natural disasters are increasingly common, agricultural production is less consistent and harder to manage, and water resources are becoming more and more scarce.
These changes, which are difficult to monitor and assess from the ground, can be devastating to industries and economies, leading to an increasing demand for space-based solutions.
At Spire, our satellites are equipped with an advanced, in-house designed GNSS receiver that powers our climate and weather products. We can process signals from all major GNSS constellations (GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, BeiDou, QZSS) and up to 32 simultaneous reflections, allowing us to offer industry-leading Earth observation capabilities.
While GNSS signals are originally meant for precise navigation, they can also be used opportunistically to sense and characterize the different layers of the Earth via their precise positioning and time synchronization capabilities.
We leverage two primary types of GNSS observations for weather and climate insights:
- GNSS-RO (Radio Occultation): As low-elevation GNSS signals traverse the Earth’s atmosphere on their way to our satellites’ antennas, they are refracted by the dense portions of the atmosphere and bend. The magnitude of this bending is dependent on the atmosphere’s temperature, pressure, and humidity content as a function of altitude. GNSS-RO data are similar to those obtained by radio sondes, except that they are acquired with unprecedented global coverage as our satellites continuously orbit the Earth, providing uniquely robust insights on the Earth’s weather.
- GNSS-R (Reflectometry): When GNSS signals are sent to Earth-bound receivers, some of the signals bounce, or reflect, off of the Earth’s surface. GNSS-R satellites are able to collect these reflections that are “imprinted” with the physical state of the surface and can be used to measure wind speed, wave height, soil moisture, and ice cover.
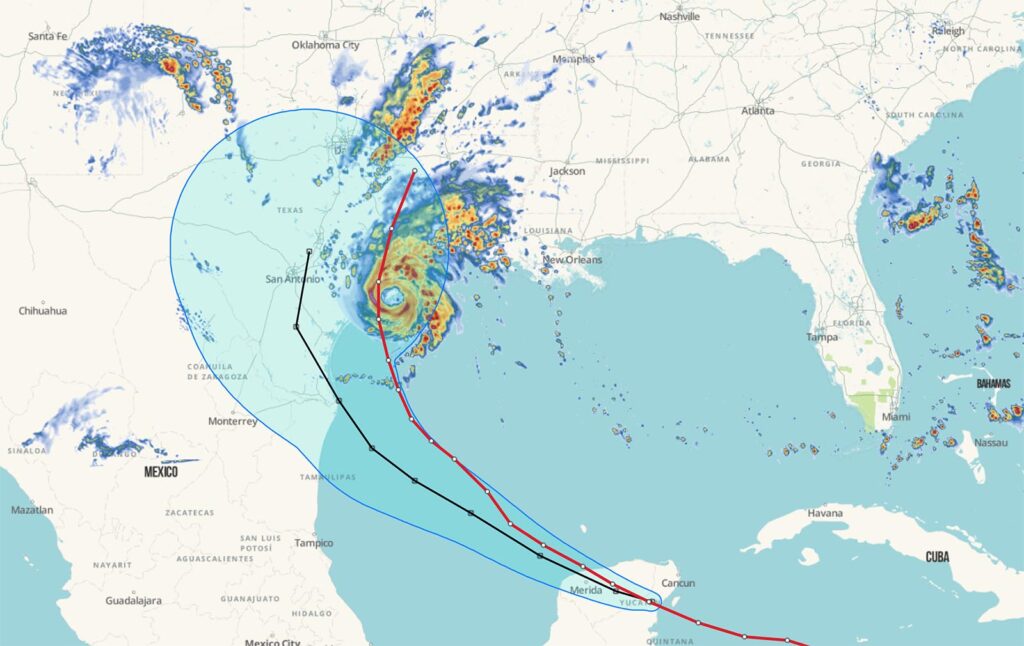
Spire’s High-Resolution Forecasting – Hurricane Beryl
Satellite constellations – FAQ
- How have satellite constellations evolved over time?
Satellite constellations today are significantly different from those deployed in the early days of space exploration. Initially designed for broad-scale purposes, early constellations focused on singular missions related to communications, weather observation, and scientific research. While effective, these constellations lacked the customization and specificity that modern applications require.
- What advancements have influenced the development of satellite constellations?
Technological advancements, particularly the miniaturization of satellites, have transformed satellite constellations over time. Near the end of the 20th century, the introduction of CubeSats marked a significant shift. These small satellites, often the size of a household microwave, allowed for quicker, more affordable development, deployment, and operation of space missions.
- What are CubeSats, and why are they important?
CubeSats are miniaturized satellites that operate in low earth orbit (LEO), a less harsh environment than medium earth orbit (MEO) or geostationary orbit (GEO). Their size and affordability have made it possible to conduct hyper-specific missions that were previously financially or operationally unfeasible.
- What are satellite clusters, and how do they function?
Satellite clusters consist of smaller groups of satellites operating in closer proximity to one another, typically in groups of 2, 3, or 4. They are designed for mission-specific data collection and real-time domain analysis. This configuration allows for enhanced data gathering and analysis across various applications.
- What applications can satellite clusters support?
Industries have begun to leverage satellite clusters for a variety of applications, including:
- Maritime logistics
- Global domain awareness
- Agricultural optimization
- National defense
- Aviation security and monitoring
- Border protection
- What are the advantages of using satellite clusters?
The rise of satellite clusters has demonstrated that industries can collect and analyze data at a more affordable cost. Additionally, these clusters can be scaled relatively easily, providing a level of flexibility in space operations that was previously unattainable.
- How do satellite clusters impact industry practices?
Satellite clusters allow industries to conduct specific missions with greater efficiency and lower costs, facilitating advancements in operational capabilities and decision-making processes across various sectors.
 Written by
Written by