ADS-B data: understanding basic regulatory context
In order to ensure successful implementation of ADS-B and for interoperability to occur globally, there are certain requirements to be met with regards to the ADS-B data that is shared between both aircraft and Air Traffic Control (ATC), and the systems in place to enable this.
In this article, we’ll take you through the current regulatory requirements for ADS-B so you’re up to speed with the latest industry mandates.
General regulations for ADS-B
ADS-B is the standard surveillance system in many countries globally and, as a result, ADS-B Out is required on all aircraft travelling through certain airspace in these regions. As of 2020, the FAA and European ADS-B mandates require that avionics and ground stations are designed to support the DO-260B (ED-102A) standard. This standard enables ATCs to provide a better service in dense traffic areas, such as the US, Europe and China, by adding information within the message that is broadcast.
In order to ensure interoperability, regions such as Asia Pacific and other areas anticipating increased air traffic, are also mandating the DO-260B standard, essentially making it the global standard.
What are the regulatory requirements around ADS-B data?
For aircraft using ADS-B Out, there is a minimum requirement around the integrity and quality of the data that is shared. The minimum set of data parameters includes information such as aircraft identification, altitude, velocity, airborne horizontal position – latitude and longitude; Special Position Identification (SPI); emergency status and surface horizontal position – latitude and longitude.
All of the data provided by the ADS-B Out system must come from approved sources, and the data transmitted by the ADS-B Out system has to originate from the same data source as used in the transponder replies to Mode S interrogations. Possible exceptions being non-transponder ADS-B beacons. Automatic data validation is usually done at ADS-B receivers to ensure the integrity of ADS-B information received from the aircraft.
When it comes to recording ADS-B data, it’s recommended that air traffic and communication service providers hold on to records for at least 30 days, in case of any accident or incident investigations that might occur.
Adapting to the standard
To meet the requirements laid out by the FAA and EASA, any new aircraft being produced must now include ADS-B Out, developed according to the DO-260B standard. Any old aircraft had to be adapted before the regulations were enforced in 2020. Depending on the existing system, this could mean anything from simply upgrading the transponder software or position source software, to something as expensive and complicated as completely replacing the transponder and position source box.
For many general aviation operators, compliance created a massive challenge – logistically and financially. As a result, the FAA launched an ADS-B rebate programme. This enabled any U.S.registered, fixed-wing, single-engine piston aircraft not already equipped with compliant ADS-B equipment by allowing them to access some of the $4.5m fund set aside to support the roll out. Over the four years of the programme, 20,000 rebates were offered.
How can Spire help operators?
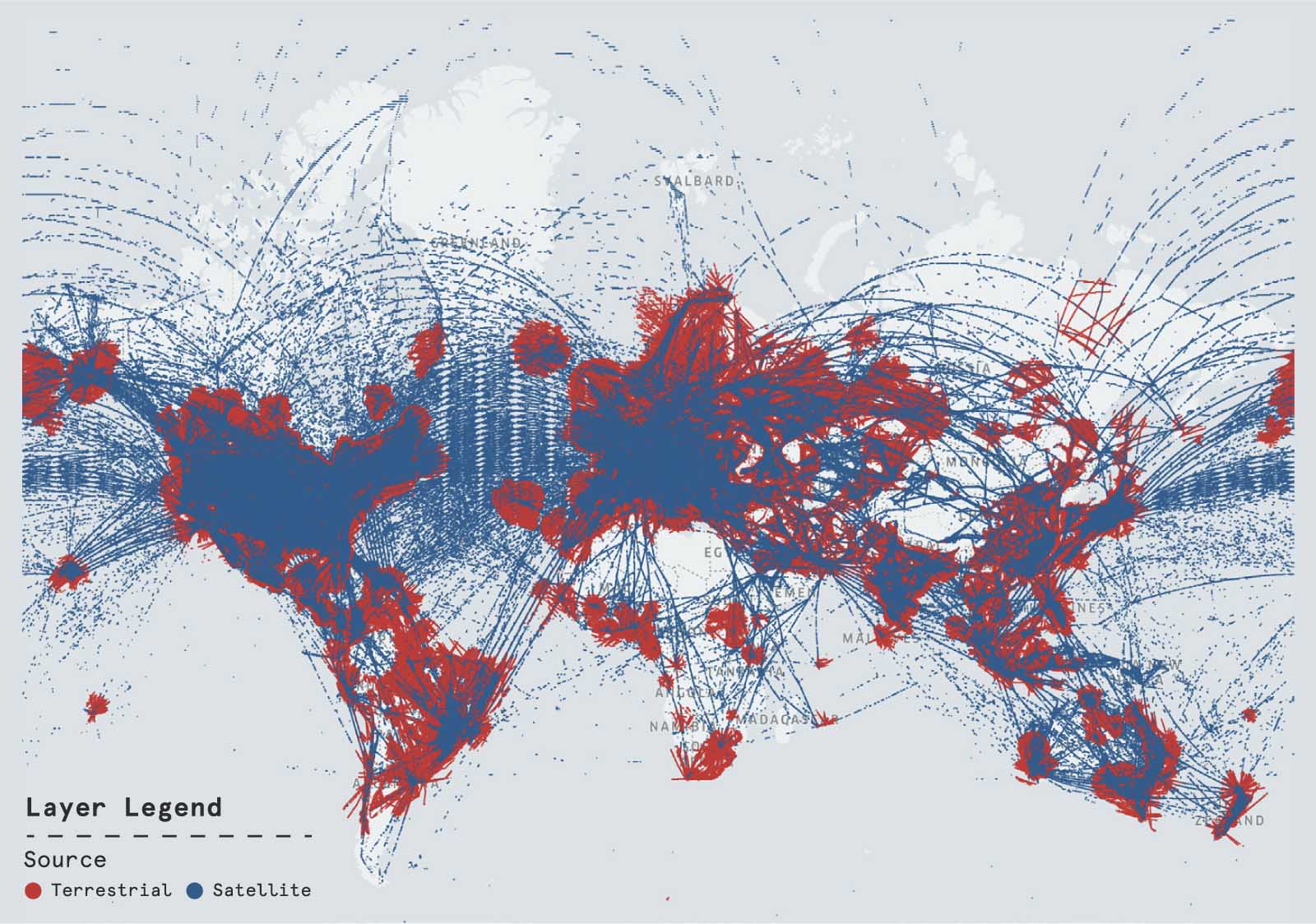
Spire Aviation is the only provider of global flight tracking data powered by a multi-use nanosatellite constellation. We offer access to both historical and real-time flight tracking and weather data to support aviation operations. Our satellite-based receivers enable us to capture data, via ADS-B signals, in remote areas that terrestrial data services cannot, such as large bodies of water or mountain ranges. This means we can provide more complete global coverage, 24/7.
Having access to more data means Spire customers can make more strategic business decisions, faster. With our flight tracking and historical data APIs, you can quickly integrate and query data into your workflows.
For more information about how Spire can help with your business needs, just give us a shout.
Continue reading our ADS-B series
01: How ADS-B has Shaped the Modern Aviation Industry
02: How does ADS-B work?
03: What is ADS-B tracking?
04: ADS-B Out and ADS-B In Explained
Current: ADS-B data: understanding basic regulatory context